Google Analytics is an incredibly useful tool for any website owner. You have the ability to measure where your site users have come from and what pages they’ve looked at. All for free. And that’s only the beginning of what Google Analytics is capable of.
That’s all pretty fabulous, but there isn’t much point in all of that amazing data if it’s wrong.
Why block yourself from Google Analytics?
As one of the most common sayings in business goes, “If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it.”
Analytics is the cornerstone for any online marketing career and is well worth understanding if you’re needing to measure your SEO strategy or want the ability to refine your marketing message.
Having analytics installed on your site can also help you measure your Technical SEO efforts, and see how long people are really prepared to hang around waiting for your page to load.
The problem with measuring anything is ensuring the data is correct.
One quandary with website analytics is making sure you don’t measure yourself. There’s not much point in trying to measure who’s visiting your site and where they’re going if you’re polluting your stats every time you visit your site. I don’t know about you, but I’m on our website multiple times a day to send people links, update articles and add events. If Google Analytics were measuring my visits, as well as legitimate visitors, our numbers would be way off.
How to block yourself from Google Analytics
Within Google Analytics there is the option of setting filters. The best way to block yourself from your own data is to set a filter to exclude yourself.
Create a new filter to exclude your IP address from being tracked
The first thing you need to do is create a new filter. This is pretty straightforward.
You must have edit permissions at the account level to be able to add filters.
- Log in to Google Analytics and navigate to the account you wish to edit
- Click on Admin at the bottom of the left sidebar (assuming you’re on a desktop or laptop)
- In the view column, click Filters

- Click the + Add Filter button. If you can’t see the button at this point, it means you do not have the permissions to create new filters.
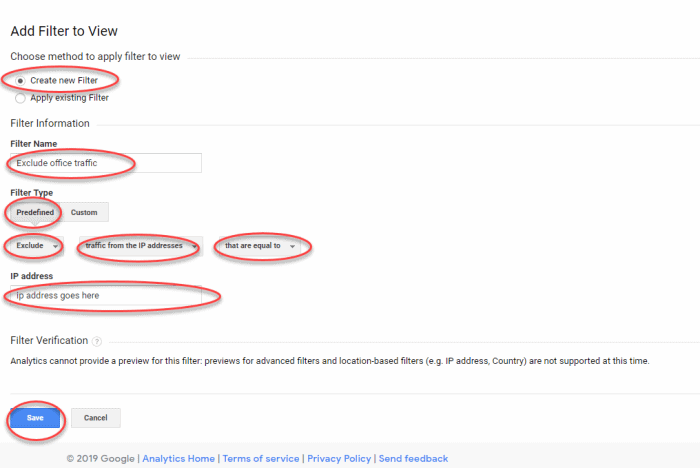
- In the Add filter to view screen:
- Select Create new Filter
- Call the filter whatever you want, but something like Exclude office traffic is a pretty good idea
- Set Filter Type to be Predefined
- Set Select filter type to Exclude
- Set Select source or destination to be traffic from the IP addresses
- Set Select expression to be that are equal to
- Quickly Google What’s my IP? to find your public IP address
- Copy and paste that IP address into the IP address text box
- Hit Save
If you work from multiple locations, then do this step for each location, and call the filter something slightly different each time, such as Exclude Brisbane office traffic and Exclude Melbourne office traffic.
Having set up your analytics to not count internal traffic, you can be assured that your data is correct and that all your visitors are real!
Pay what you like for our "SEO for Australian Small Business" eBook
Thanks for reading How to not track yourself in Google Analytics.
In recognition of the small businesses who have been doing it tough in recent times, you can now pay what you like for our SEO for Australian Small Business eBook.
Minimum price is $5
Check out SEO for Australian Small Business